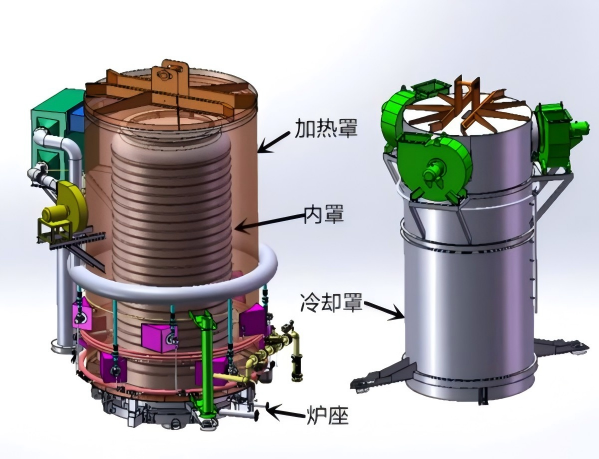
Working principle of the bell-type furnace
The shielded furnace is a common heating equipment used in industrial production. Its working principle is to place the heating elements inside a sealed furnace chamber, and utilize the high-temperature heat generated by electricity or the combustion of gas to heat the objects.
The shielded furnace mainly consists of the furnace body, heating elements, control system, and furnace door, etc. The furnace body is usually made of materials such as heat-resistant steel, refractory bricks, or refractory fibers. The heating elements can be resistors, electric heating tubes, or burners, and different heating elements are selected according to different heating methods. The control system is used to control parameters such as heating power, temperature, and heating time to ensure the stability and controllability of the heating process. The furnace door is used to open and close the furnace chamber, facilitating the loading and unloading of objects and maintenance.
During operation, the shielded furnace first heats the heating elements to the set temperature, then places the object to be heated in the furnace chamber, and closes the furnace door. The heating elements then start to transfer heat to the object, causing its temperature to gradually increase. Usually, there is an exhaust port at the top of the furnace body to discharge the exhaust gas and smoke produced by combustion, maintaining a clean environment inside the furnace. The control system automatically adjusts the heating power and heating time according to the set heating curve to achieve the desired heating effect.
The working principle of the shielded furnace can be divided into two types: radiation heating and convection heating. Radiation heating refers to the heating elements transferring heat to the object through radiation, causing the surface temperature of the object to increase. This heating method is suitable for objects that require high-temperature heating, such as the sintering, melting, and heat treatment of metal materials. Convection heating refers to the heating elements generating heat through convective heat transfer to the object, causing the object's temperature to increase. This heating method is suitable for objects that require uniform heating, such as annealing, quenching, and tempering of metal materials, etc.
HEXIN MACHINERY specializes in manufacturing various shielded furnaces and reaction vessels, such as industrial heating equipment. It has a skilled team and can provide custom processing based on drawings or according to customer requirements.